JAVA集合学习之Set篇
JAVA集合学习之Set篇
1. set接口和常用方法
1.1 set接口基本介绍
无序(添加和取出的顺序不一致),没有索引,注意:取出的顺序虽然不是添加的顺序,但是它是固定的。
不允许重复元素,所以最多包含一个null
JDK API中Set接口的实现类有
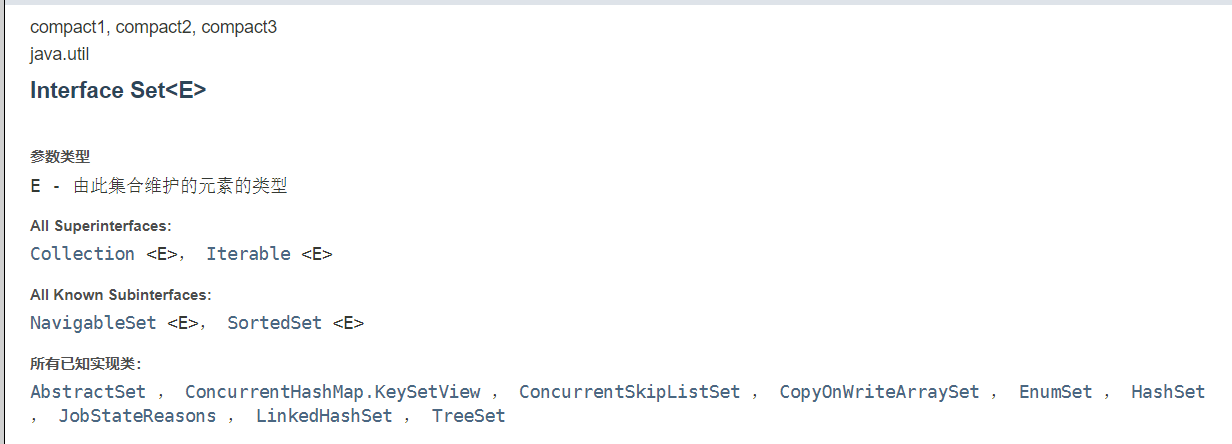
1.2 set接口常用方法
和List接口一样,set接口也是Collection的子接口,因此,常用方法和Collection接口一样
1.3set接口的遍历方式
同Collection的遍历方法一样,因为set接口是Collection接口的子接口。
- 可以使用迭代器
- 增强for
- ==不能使用索引的方式遍历==
1 | |

2.HashSet
2.1Hash基本介绍
HashSet 实现了Set接口
HashSet 实际上是HashMap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7/**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}可以存放null值,但是只能有一个null
HashSet不保证元素是有序的,取决于hash值,再确定索引的结果
不能有重复元素/对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61package com.hspedu.set_;
import java.util.HashSet;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class HashSet01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
//说明
//1. 在执行add方法后,会返回一个boolean值
//2. 如果添加成功,返回 true, 否则返回false
//3. 可以通过 remove 指定删除哪个对象
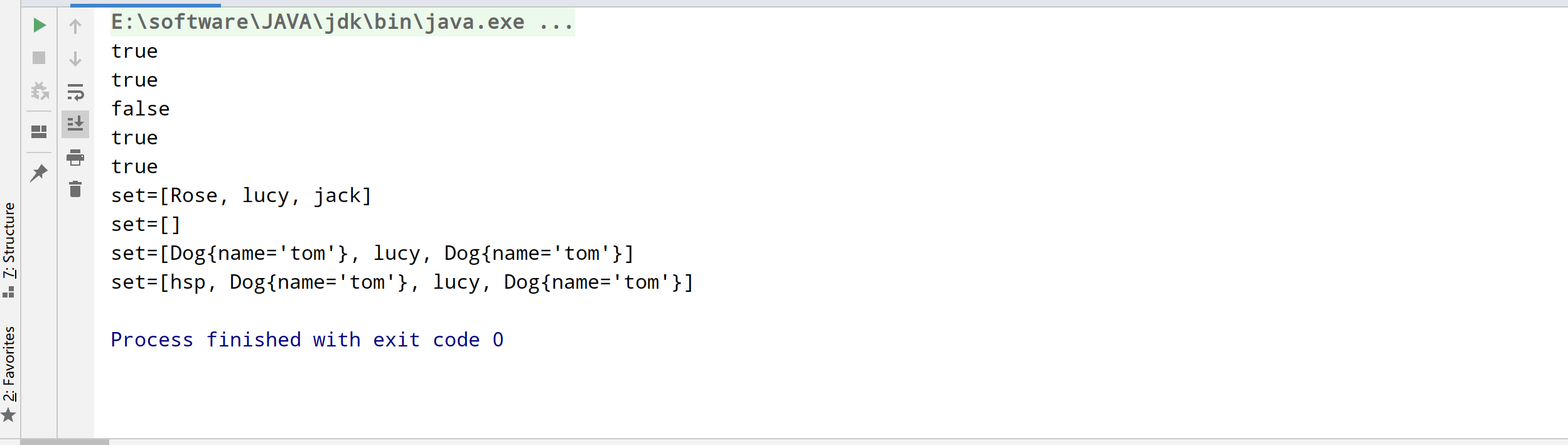
System.out.println(set.add("john"));//T
System.out.println(set.add("lucy"));//T
System.out.println(set.add("john"));//F
System.out.println(set.add("jack"));//T
System.out.println(set.add("Rose"));//T
set.remove("john");
System.out.println("set=" + set);//3个
//
set = new HashSet();
System.out.println("set=" + set);//0
//4 Hashset 不能添加相同的元素/数据?
set.add("lucy");//添加成功
set.add("lucy");//加入不了
set.add(new Dog("tom"));//OK
set.add(new Dog("tom"));//Ok
System.out.println("set=" + set);
//在加深一下. 非常经典的面试题.
//看源码,做分析, 先给小伙伴留一个坑,以后讲完源码,你就了然
//去看他的源码,即 add 到底发生了什么?=> 底层机制.
set.add(new String("hsp"));//ok
set.add(new String("hsp"));//加入不了.
System.out.println("set=" + set);
}
}
class Dog { //定义了Dog类
private String name;
public Dog(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
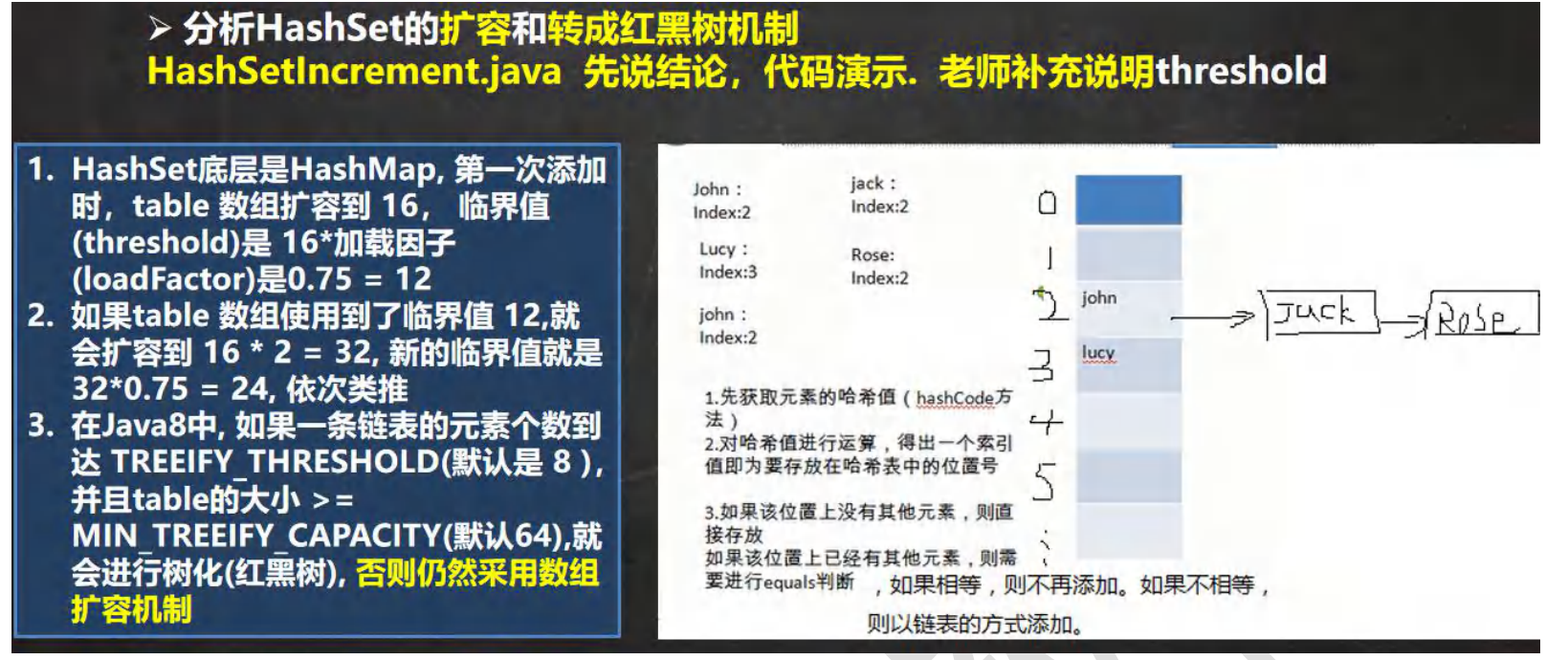
2.2HashSet 底层机制
HashSet 底层是HashMap,HashMap底层是(数组+链表+红黑树)

2.3模拟底层简单结构
结构:
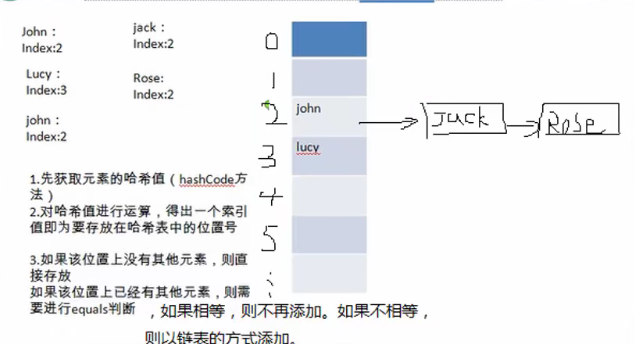

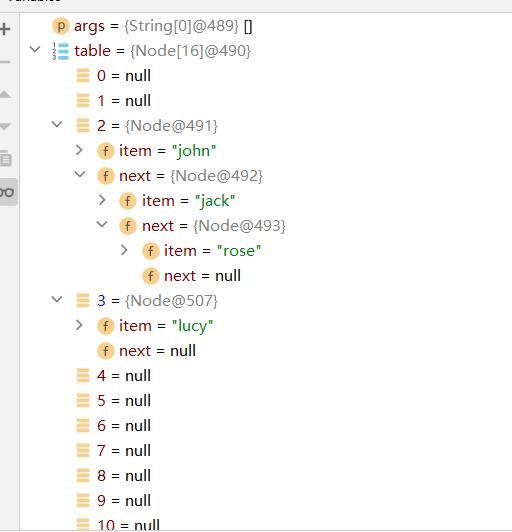
1 | |
2.4HashSet add()方法底层
- HashSet 底层是 HashMap
- 添加一个元素时,先得到hash值 会转成 -> 索引值
- 找到存储数据表table,看这个索引位置是否已经存放的有元素
- 如果没有,直接加入
- 如果有,调用 equals() 比较, 如果想同,就放弃添加,如果不相同,则添加到最后
- 在 java8 中,如果一条链表的元素个数到达 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是8),并且table的大小 >= MIN_TREEIFY_CAPCAITY(默认64),就会进行树化(红黑树)
1 | |
2.4.1 底层源码分析
创建hashset对象,构造器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7/**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing <tt>HashMap</tt> instance has
* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}执行add()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15/**
* Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present.
* More formally, adds the specified element <tt>e</tt> to this set if
* this set contains no element <tt>e2</tt> such that
* <tt>(e==null ? e2==null : e.equals(e2))</tt>.
* If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set
* unchanged and returns <tt>false</tt>.
*
* @param e element to be added to this set
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set did not already contain the specified
* element
*/
public boolean add(E e) { // e:"java"
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null; //e:"java" map:"{}" (static) PRESENT = new Object
}执行put()方法,该方法会执行hash(key)方法,得到key对应的hash值(不是hashcode,通过算法计算hash值,降低hash冲突的几率)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) { // key:"java" value:PRESENT/Object@502
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); // key:"java" value:PRESENT/Object@502
}hash(key)方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20/**
* Computes key.hashCode() and spreads (XORs) higher bits of hash
* to lower. Because the table uses power-of-two masking, sets of
* hashes that vary only in bits above the current mask will
* always collide. (Among known examples are sets of Float keys
* holding consecutive whole numbers in small tables.) So we
* apply a transform that spreads the impact of higher bits
* downward. There is a tradeoff between speed, utility, and
* quality of bit-spreading. Because many common sets of hashes
* are already reasonably distributed (so don't benefit from
* spreading), and because we use trees to handle large sets of
* collisions in bins, we just XOR some shifted bits in the
* cheapest possible way to reduce systematic lossage, as well as
* to incorporate impact of the highest bits that would otherwise
* never be used in index calculations because of table bounds.
*/
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); // >>> 无符号右移16位,降低hash冲突的几率
}==putVal()方法==
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods.
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K, V>[] tab;
Node<K, V> p;
int n, i; //定义了辅助变量
//table 就是 HashMap 的一个数组,类型是 Node[]
//if 语句表示如果当前table 是null, 或者 大小=0
//就是第一次扩容,到16个空间.
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//(1)根据key,得到hash 去计算该key应该存放到table表的哪个索引位置
//并把这个位置的对象,赋给 p
//(2)判断p 是否为null
//(2.1) 如果p 为null, 表示还没有存放元素, 就创建一个Node (key="java",value=PRESENT)
//(2.2) 就放在该位置 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null)
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
//一个开发技巧提示: 在需要局部变量(辅助变量)时候,在创建
Node<K, V> e;
K k; //
//如果当前索引位置对应的链表的第一个元素和准备添加的key的hash值一样
//并且满足 下面两个条件之一:
//(1) 准备加入的key 和 p 指向的Node 结点的 key 是同一个对象
//(2) p 指向的Node 结点的 key 的equals() 和准备加入的key比较后相同
//就不能加入
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//再判断 p 是不是一颗红黑树,
//如果是一颗红黑树,就调用 putTreeVal , 来进行添加
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K, V>) p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {//如果table对应索引位置,已经是一个链表, 就使用for循环比较
//(1) 依次和该链表的每一个元素比较后,都不相同, 则加入到该链表的最后
// 注意在把元素添加到链表后,立即判断 该链表是否已经达到8个结点
// , 就调用 treeifyBin() 对当前这个链表进行树化(转成红黑树)
// 注意,在转成红黑树时,要进行判断, 判断条件
// if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(64))
// resize();
// 如果上面条件成立,先table扩容.
// 只有上面条件不成立时,才进行转成红黑树
//(2) 依次和该链表的每一个元素比较过程中,如果有相同情况,就直接break
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(8) - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
//size 就是我们每加入一个结点Node(k,v,h,next), size++
if (++size > threshold)
resize();//扩容
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
2.4.2 源码补充说明
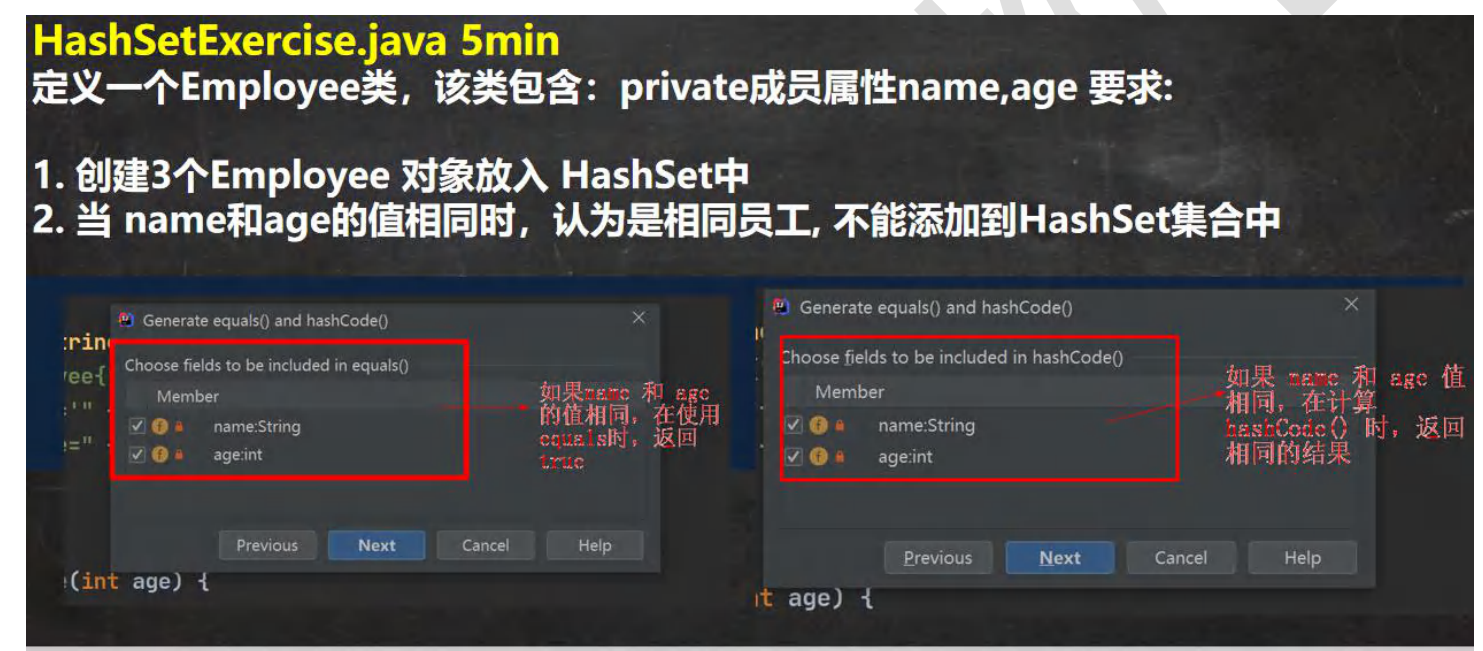
要实现当name和age的值相同时,就是同一个员工,重写hashCode方法和equals方法
2.5 LinkedHashSet
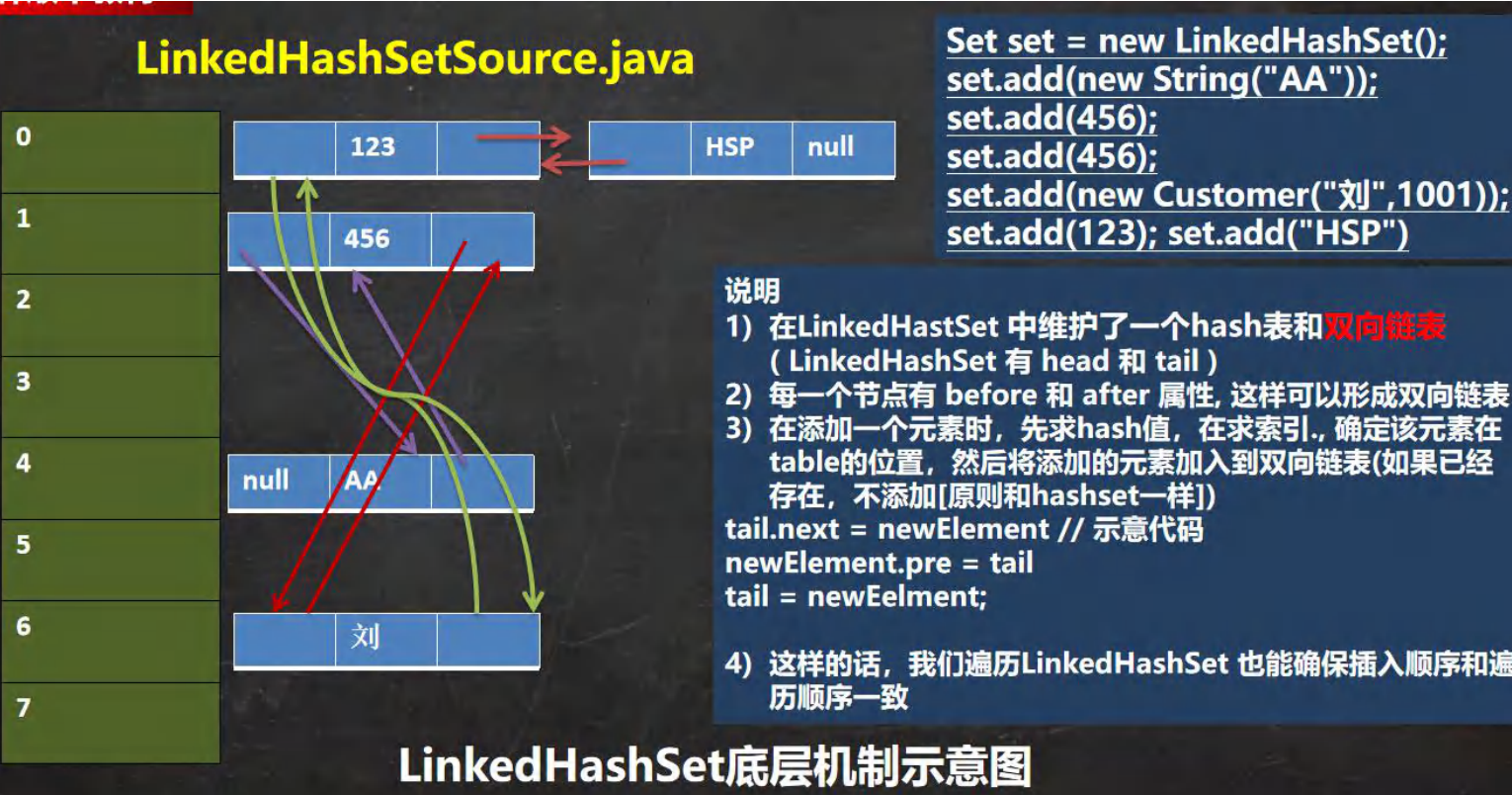
2.5.1LinkedHashSet 的全面说明
LinkedHashSet是HashSet的子类
LinkedHashSet底层是一个LinkedHashMap,底层维护一个 数组+双向链表
LinkedHashSet根据元素的hashCode值来决定元素的存储位置,同时使用链表维护元素的次序,这使得元素看起来是以插入顺序保存的
LinkedHashSet不允许添加重复元素
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!